1. MEDICATIONS
Medications help in managing problems with walking, movement and tremor. The medications increase or substitute for the lack of chemical required for motor movements by replacing it with a specific signaling chemical in the patient’s brain.
The medications provided by the doctors are:
(a) General medication –
The most effective Parkinson’s disease medication, is a natural chemical that passes into the patient’s brain and is converted to essential hormone for proper motor movements.
(b) Agonists –
Unlike the general medications, agonists don’t change into the brain hormones completely. Instead, they replicate their effects in the patient’s brain. Agonists include pramipexole, ropinirole and rotigotine. A short-acting inject-able agonist, apomorphine, is usually used for quick relief..
(c) MAO-B inhibitors –
These medications include Selegiline and Rasagiline. They help prevent the breakdown of brain hormones by inhibiting the brain enzyme monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B).
(d) Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) Inhibitors –
Entacapone is the primary medication. This medication mildly prolongs the effect of therapy by blocking an enzyme that breaks down brain hormones.
(e) Anticholinergics –
These medications were used for many years to help control the tremor associated with Parkinson’s disease.
(f) Amantadine –
Doctors prescribe Amantadine alone to provide short-term relief of symptoms of mild, early-stage Parkinson’s disease. It may also be given with therapy during the later stages of Parkinson’s disease to control involuntary movements also known as dyskinesia induced with general medication.
2. SURGICAL METHODS
DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION(DBS)
As Parkinson’s is a disease with no cure as of now and it’s said to be the end, but with the Deep Brain Stimulation(DBS) therapy there’s a new hope for the patients in improving their quality of living by easing the symptoms that they have to go through due to Parkinson’s. Deep Brain Stimulation therapy for Parkinson’s treatment is a huge step towards living a more independent life. Under your doctor’s guidance, you will be able to gradually return to your usual activities which got restricted due to Parkinson’s Disease. Deep brain stimulation is an established treatment for movement disorders, such as essential tremor, Parkinson’s disease and Dystonia and more recently, Obsessive-Compulsive-Disorder (OCD). This treatment is reserved for people who aren’t able to get control of their symptoms with medications.
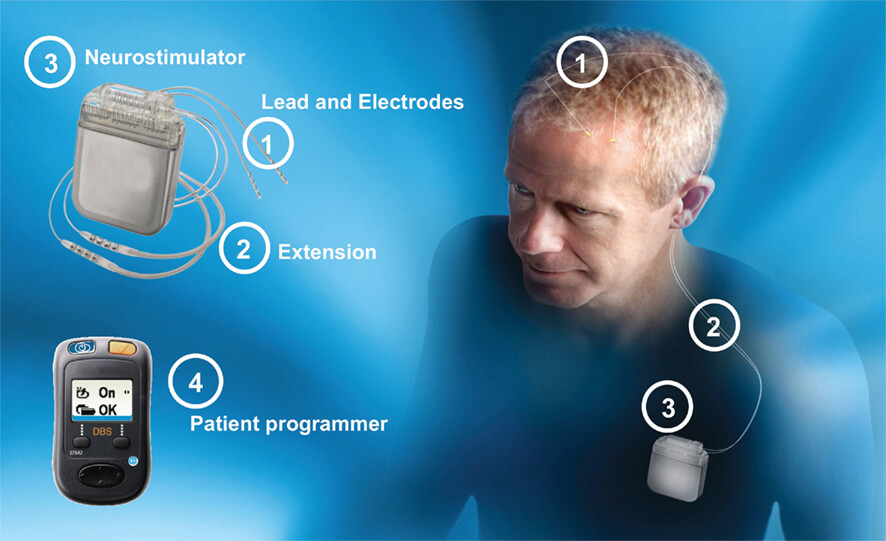
In Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), surgeons implant electrodes into a specific part of your brain. The electrodes are connected to a pulse generator/battery implanted in your chest near your collarbone that sends electrical pulses to your brain and may reduce your Parkinson’s disease symptoms.DBS directly changes brain activity in a controlled manner. DBS involves minimal permanent surgical changes to the brain. Instead, the procedure uses electrical stimulation to regulate electrical signals in neural circuits to and from identified areas in the brain to improve PD symptoms.
In general this is how the Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery works:
(a)Lead Placement –
The expert care team fits the patient with a special head frame to keep the head still during the procedure. Then, they use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to map your brain and identify the area in your brain where they’ll place the electrodes.
The patient will be given a local anesthetic to numb the scalp before surgery, but won’t need an anesthetic in the brain itself because the brain has no pain receptors.
Your surgeon implants a thin wire lead with a number of electrodes at the tips into a specific area of your brain. Or, one lead is implanted into each side of the brain. A wire runs under the skin of the patient to a pulse generator called the neuro-stimulator implanted near the collarbone.
In most cases, the patient will remain awake and alert during the procedure so that their respective neurologist can talk to the patient to make sure the right areas of the patient’s brain are being stimulated. The responses of the patient help the health care team place the lead in the correct place while minimizing side effects.
During surgery, both the neurologist and neurosurgeon carefully monitor the brain of the patient to help ensure correct electrode placement.
(b)Pulse generator/battery Placement –
During the second portion of the surgery, which may occur on the same day or at a later time, the surgeon implants the part of the device that contains the batteries under the skin in the patient’s chest, near the collarbone. General anesthesia is used during this procedure. Wires from the brain electrodes are placed under the patient’s skin and guided down to the battery-operated pulse generator. The generator is programmed to send continuous electrical pulses to the brain. The patient controls the generator, and can turn it on or off using a special remote control.
A few weeks after surgery, the pulse generator in the chest is activated in the doctor’s office. The doctor can easily program the patient’s pulse generator from outside the body using a special remote control. The amount of stimulation is customized to patient’s condition. Stimulation may be constant, 24 hours a day, or the doctor may advise the patient to turn the pulse generator off at night and back on in the morning, depending on the patient’s condition. You can turn stimulation on and off with a special remote control that the patient takes home with him. In some cases, the doctor may program the pulse generator to let the patient make minor adjustments at home.
The battery life of the patient’s generator varies with usage and settings. When the battery needs to be replaced, the respective surgeon will replace the generator during an outpatient procedure.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson’s disease offers a multitude of benefits, from increased control to reduced medications.
Some of the major benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation that sets it apart from the other medications are:
1. Symptom reduction-
DBS often reduces symptoms significantly. These include motor symptoms like stiffness, tremor, slowness and dyskinesia. DBS has also been shown to aid in on/off fluctuations, improve quality of life, and increase overall energy level.
2. Little to no damage –
In contrast to previously used surgical methods, DBS does not damage portions of the brain, nor remove nerve cells.
3. Decreased Medication Needs –
Utilizing DBS in addition to general medication could decrease a person’s need for medication, thus, decreasing medication access and cost issues, as well as side effects.
4. Individualized Treatment –
Electrodes and stimulation frequency and intensity can be controlled by physicians and the individual with DBS, and can be subjectively altered when needed.

















